

Next: Evolvable hardware (EH)
Up: E
Previous: Evolutionary programming (EP)
Evolution strategy (ES)
variant of EA, which generally operates on the ``natural'' problem
representation (no genotype-phenotype mapping for
object parameters).
The basic types of ES are classified using the
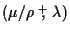 -ES
(pronounced: ``mu-slash-rho-plus-(or)-comma-lambda-ES'') notation.
Here
-ES
(pronounced: ``mu-slash-rho-plus-(or)-comma-lambda-ES'') notation.
Here 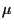 is the number of parents,
is the number of parents, 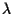 is the number of
offspring and
is the number of
offspring and 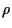 is the mixing number (the number of parents
which take part in the (multi-) recombination process to produce one
offspring); ``
is the mixing number (the number of parents
which take part in the (multi-) recombination process to produce one
offspring); ``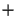 '' or ``,'' determines the type of
truncation selection.
An individual consists of a set of object parameters, the
corresponding value of the
objective function
and a set of
(endogenous)
strategy parameters.
The ES employs
mutation and
recombination
(if
'' or ``,'' determines the type of
truncation selection.
An individual consists of a set of object parameters, the
corresponding value of the
objective function
and a set of
(endogenous)
strategy parameters.
The ES employs
mutation and
recombination
(if 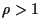 ) as variation operators.
) as variation operators.
Hans-Georg Beyer
2002-02-25